|
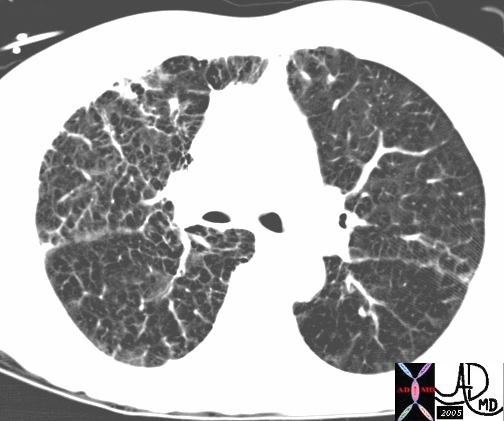
Crazy Paving in Lung Disease Copyright 2008 Ashley Davidoff MD Crazy Paving Pattern is defined as scattered or diffuse ground-glass attenuation with superimposed interlobular septal thickening and intralobular lines. When the pattern of “crazy-paving” is present, alveolar proteinosis is most likely but lipoid pneumonia, bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, and pneumocystis pneumonia are included in the differential diagnosis.
This 74 year old female with severe COPD preents with increasing shortnes of breath. There were extensive changes of interlobular septal thickening of the lungs bilaterally with ground glass changes in the left upper lobe. the cause of the “crazy paving in this instance was not known but thought to represent an non specific interstitial pneumonitis. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
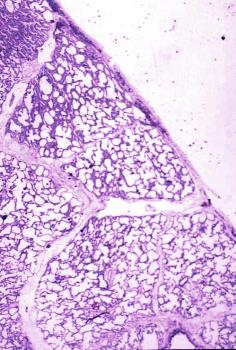
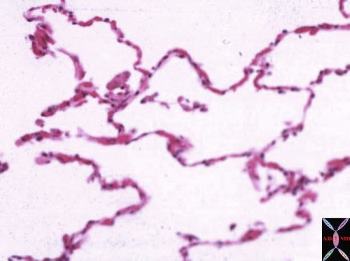
Pathologic Findings: Interlobular Septal Thickening and Ground Glass Opacity
Pathologic Findings: Alveolar Edema Interlobular septal thickening Causes INFECTION – pneumocystis INFLAMMATION – – ARDS – sarcoidosis – non specific interstitial pneumonia NSIP – organizing pneumonia – lipoid pneumonia (inhalational) NEOPLASM – mucinous alveolar carcinoma CIRCULATORY – pulmonary hemorrhage syndromes IDIOPATHIC – pulmonary alveolar proteinosis PAP
Pearls: Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is most common in adults between 20 and50 years of age. Dyspnea and nonproductive cough are the most common associated symptoms. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) and Organizing pneumonia may be induced by Methotrexate, Amiodarone or Bleomycin. Honeycombing is typically absent. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is characterized by a lepidic growth pattern through the airways and air spaces with preservation of the lung architecture. References: “Crazy-Paving” Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: Radiologic-Pathologic Overview, Radiographics 2003;23:1509-1519 Crazy-paving Appearance at Thin-Section CT: Spectrum of Disease and Pathologic Findings, Radiology 1999 CT-Pathology Correlations: http://pathhsw5m54.ucsf.edu/ctpath/ctpath23.html 5* /MA. |