Copyright 2008
Ashley Davidoff MD
The ground-glass pattern is defined as the hazy increase in lung opacity that does not obscure the lung markings. ( image) Virginia
Caused by changes in the interstitium (interlobular septa alveolar membrane and capillaries ) or in the alveoli In the capillaries it may be caused by increased capillary volume, while in the interlobular septa it may be caused by early interstitial lung disease. Both inflammatory changes and fibrosis may be present. In the alveoli may be caused by partial collapse
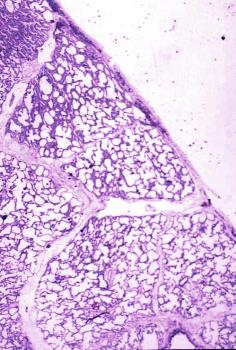
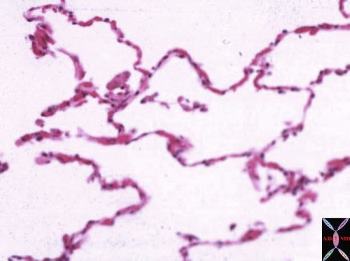
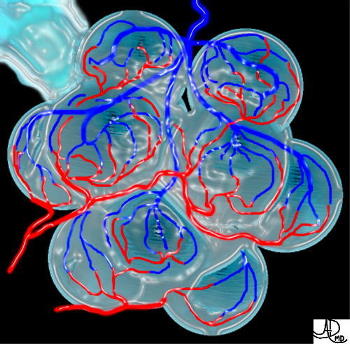
32649b 32164
About 50% of cases are due to interstitial disease, 25% due to capillary causes and 25% mixed. It usually implies active disease and potentially treatable disease.
Acute diseases
early CHF
early pneumonia
ARDS
Acute interstitial pneumonia
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
Viral pneumonias
Early interstitial lung disease
Acute eosinophilic pneumonia
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis •
Subacute or chronic causes
subacute stage of extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Approximately 50% of patients also have ill-defined nodules, 1-5 mm in diameter.
hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
interstitial lung diseases (NSIP, DIP)
Less common causes include
bronchoalveolar carcinoma
alveolar proteinosis
desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) and
alveolar proteinosis.
sarcoidosis
PEARLS
In patients with AIDS and acute respiratory symptoms, the presence of new ground glass changes usually implies P Carinni pneumonia.
The presence of ground glass usually implies acute treatable disease, unless there are other changes that infer fibrosis (traction, honeycombing)
A ground-glass pattern is also seen in the active phase of fibrosing alveolitis where it is usually associated with characteristic subpleural fibrosis. “”” ANATOMICAL and PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Ground glas appearance is caused by partial volume artifact and therefore on thick section CT where partial artifact is greater, false positivity is rife. Therefore the finding should only be made on HRCT
Web References