Definition
MRI is an imaging technique that utilizes a strong magnetic field to align protons in the body. Specific pulse sequences produced by a radiofrequency electromagnetic pulse reorient the protons. When the RF pulse is turned off, the spinning protons relax back in a tissue specific manner (time) to their equilibrium state that is characteristic and unique to the tissue. This data is detected, recorded, and converted into a format that is reflected as an image.
The advantages of MRI are that it does not involve ionizing radiation and it is a safe non invasive procedure.
It does require the patient to lie quite and still for prolonged periods (30-45 minutes), and is currently contraindicated in patients who have pacemakers, and other metal implants such as cochlear implants.
The contrast resolution of MRI is superior to CT and is made possible by a variety of pulse sequences (5-20 per study) that enable the contrast differences between two tissues to be enhanced. Contrast agents are usually used in oncological imaging, unless contraindicated by renal compromise) and further enable the distinction and characterization of malignant tissue.
Character
|
T1
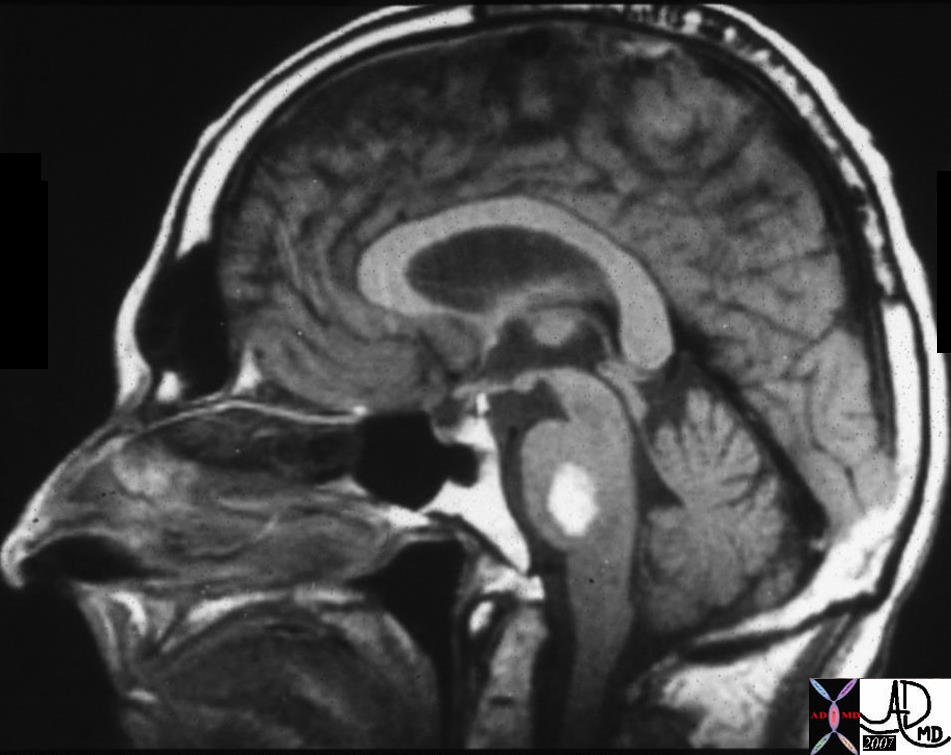
Anterior and Posterior Commissures |
| 21731 brain fx mass dx metastasis dx melanoma MRI T1 sagittal Courtesy James Donnelly MD Uploaded RP |
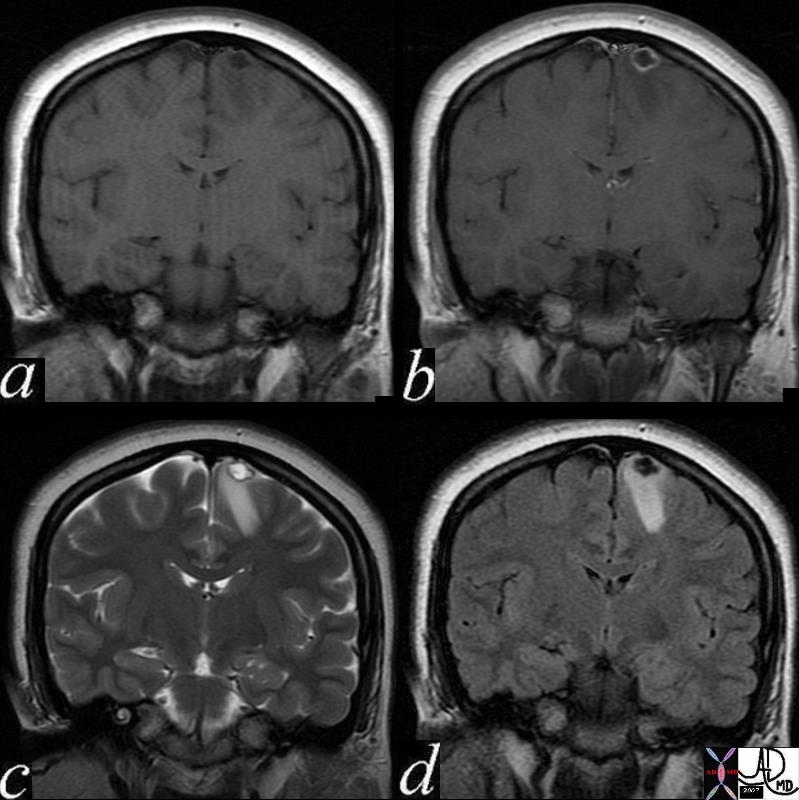
Cysticercosis
|
| 71575c02 24 female presents with seizures brain cortex vertex parafalcine falx fx nodule 9mm ring thinly enhancing lesion left frontal lobe with tiny mural nodule which enhances as well rim T2 hypointense ? calcification nodule T2 hyperintense white matter edema edema right frontal lobe a = T1 pre gadolinium precontrast b= T1 – post contrast post gadolinium c= T2 weighted image d = FLAIR dx cysticercosis infection Courtesy Davidoff MD |
T2

Cysticercosis
|
| 71575c02 24 female presents with seizures brain cortex vertex parafalcine falx fx nodule 9mm ring thinly enhancing lesion left frontal lobe with tiny mural nodule which enhances as well rim T2 hypointense ? calcification nodule T2 hyperintense white matter edema edema right frontal lobe a = T1 pre gadolinium precontrast b= T1 – post contrast post gadolinium c= T2 weighted image d = FLAIR dx cysticercosis infection Courtesy Davidoff MD |
FLAIR
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery, (FLAIR) is an inversion recovery sequence that reflects an increase in interstitial water content such as brain tumors, cerebral infarcts, and gliotic scars. It is used to null signal from fluids, so that free fluid is dark and edematous tissue is bright.. In the brain it may be used to suppress CSF to facilitate imaging periventricular disease such as multiple sclerosis.

Cysticercosis
|
| 71575c02 24 female presents with seizures brain cortex vertex parafalcine falx fx nodule 9mm ring thinly enhancing lesion left frontal lobe with tiny mural nodule which enhances as well rim T2 hypointense ? calcification nodule T2 hyperintense white matter edema edema right frontal lobe a = T1 pre gadolinium precontrast b= T1 – post contrast post gadolinium c= T2 weighted image d = FLAIR dx cysticercosis infection Courtesy Davidoff MD |
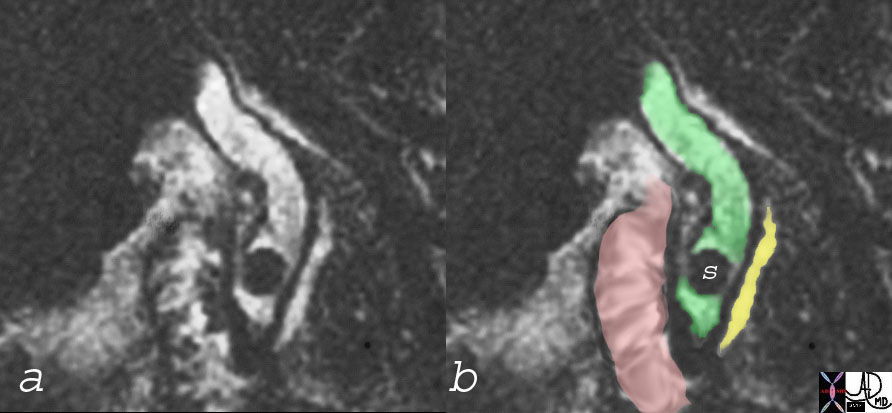
MRCP with Stone (S) in Bile Duct (green) and Normal PAncreatic Duct (yellow) and Duodenum (pink)
|
| 17088c03 bile duct stone choledocholithiasis dilated CBD pancreatic duct duodenum MRCP MRI Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
GRE
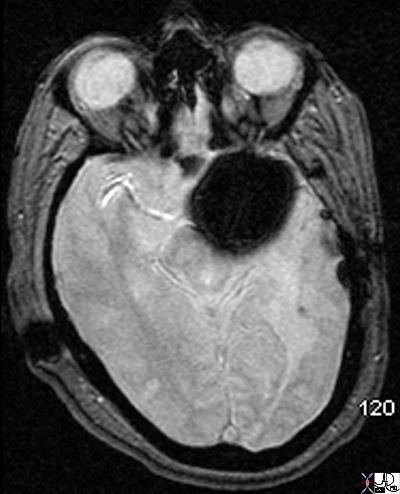
Dark Blooming Signal GRE
|
| 71542 50 M s/p clipping of MCA aneurysm brain middle cerebral artery cerebrum fx clip artifact artifact from subcutaneous V-P shunt fx metallic density GRE T2 star effect MRI Davidoff MD 71542c02 |
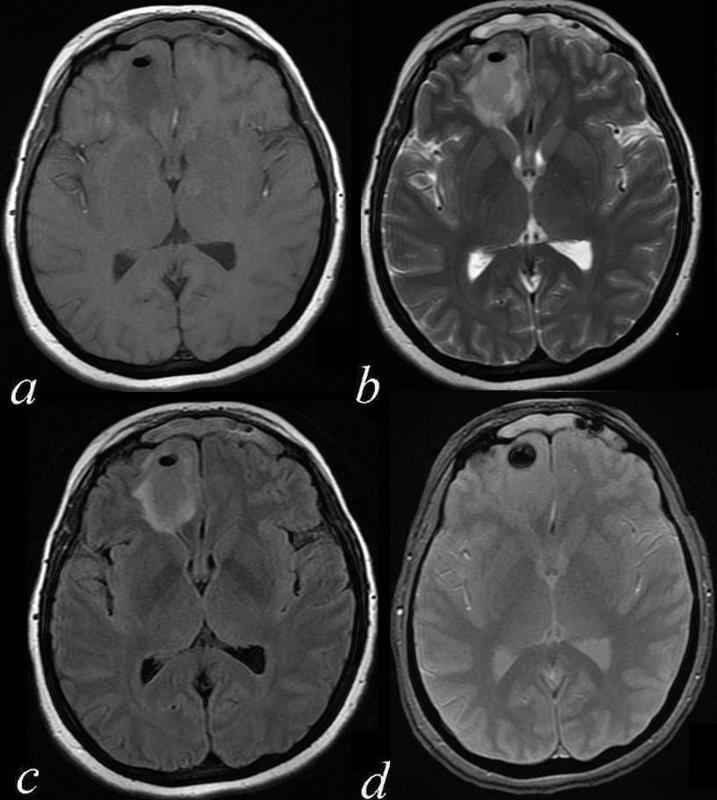
Metallic Clip GRE Blooming T2 star
|
| 71542c02 50 M s/p clipping of MCA aneurysm brain middle cerebral artery cerebrum fx clip artifact artifact from subcutaneous V-P shunt a= CTscan b = T2 weighted image c= FLAIR d = GRE fx metallic density GRE T2 star effect MRI Davidoff MD |
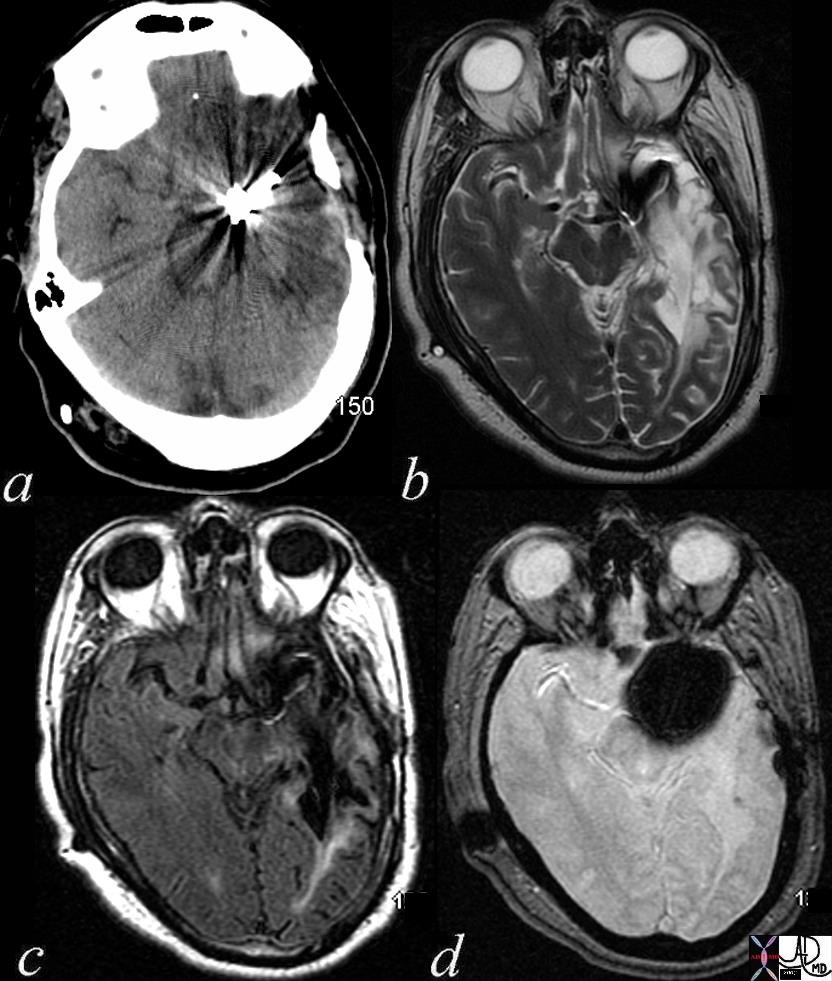
AIR
Air in a Brain Abscess – T1 T2 FLAIR GRE
|
| 71604.c02b 40 year old female with headache brain maxillary sinus frontal lobe fx air fluid level parafalcine falx cerebri a= T1 weighted b= T2 weighted c = FLAIR d= GRE dx left maxillary sinusitis with brain abscess air fluid level thickened mucosa of maxillary sinus MRI Davidoff MD 71604.c02 71604.c03 71604.c04 71604.c02b |
Water
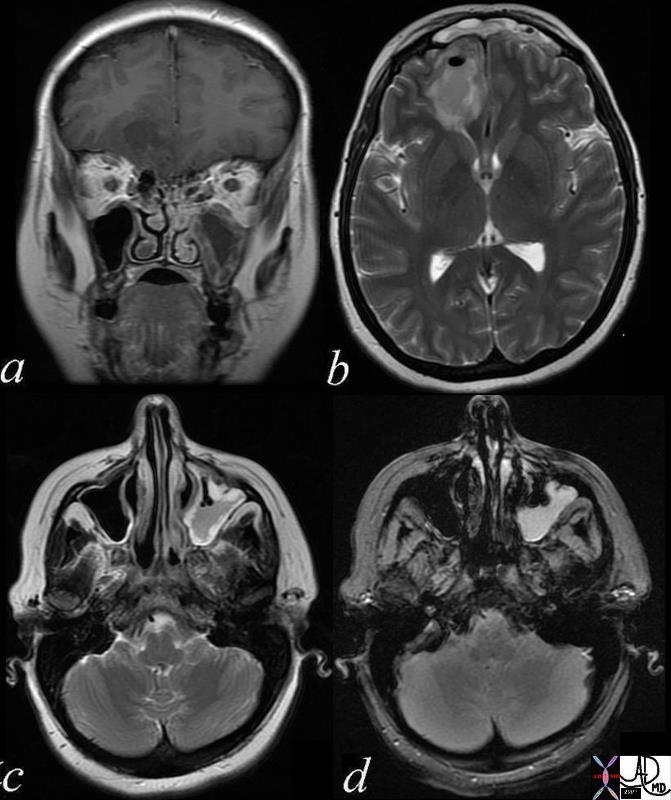
Left Maxillary Sinusitis Complicated by Brain Abscess – MRI
|
| 71604.c03 40 year old female with headache brain maxillary sinus frontal lobe fx air fluid level parafalcine falx cerebri a= T1 weighted b= T2 weighted c = T2 weighted d= FLAIR dx acute on chronic left maxillary sinusitis with brain abscess air fluid level thickened mucosa of maxillary sinus MRI Davidoff MD 71604.c02 71604.c03 71604.c04 71604.c02b |
CNS

Acute and Chronic Infarction with CT and DWI MRI |
| 49679c01 brain DWI occipital lobe fx vague hypodensity right occipital lobe with encephalomalacia and ex vacuo changes in the left occipital and posterior parietal region dx acute infarction right occipital lobe chronic infarction left occipital lobe CTscan high intesity in right occipital lobe and low intensity in left occipitoparietal region dx acute infarction right occipital lobe chronic infarction left occipital lobe MRI diffusion weighted imaging Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
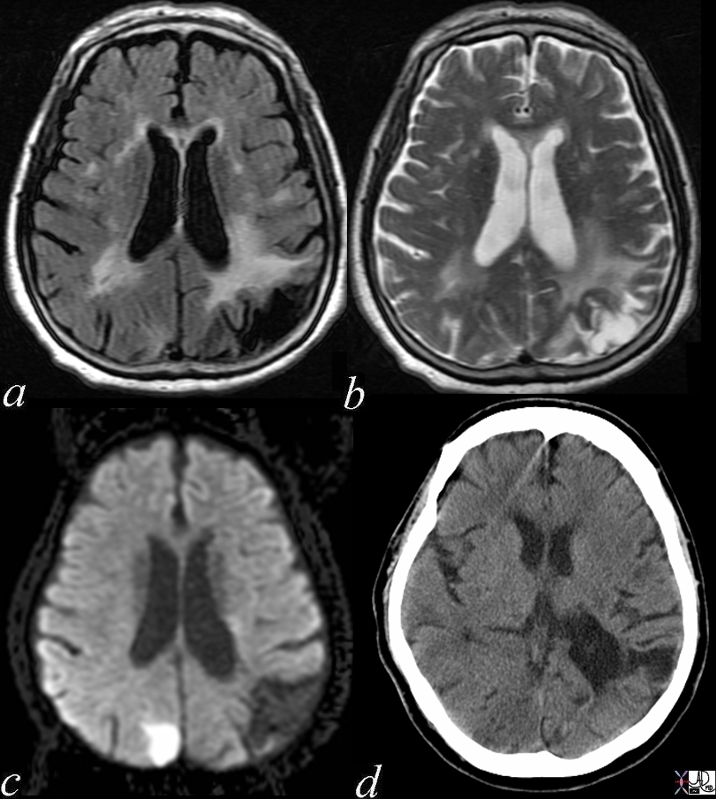
Acute and Chronic Infarction |
| 49685C01 brain DWI occipital lobe fx vague hypodensity right occipital lobe with encephalomalacia and ex vacuo changes in the left occipital and posterior parietal region dx acute infarction right occipital lobe chronic infarction left occipItoparietal lobe a IR white matter disease vague increase in right b T2 gliosis left parietal c DWI bright acute right occipital d CT vague hypodensity right occipital old infarct left dx acute infarction right occipital lobe chronic infarction left parietal lobe MRI diffusion weighted imaging CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
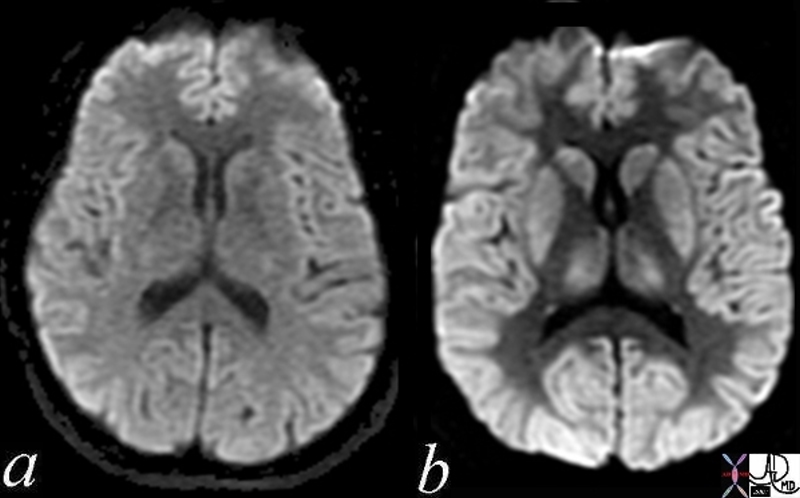
Normal and Global Ischemia after Cardiac Arrest |
| The two images represent a diffusion weighted MRI image which measures Brownian motion of molecules. In acute infarction there is restricted Bronian motion of the affected area and the image can be manipulated to present this a s a bright region. In this case the acute infarction or ischemia (b) is relatively bright compared to the white namatter and compared to the gray matterof the normal (a)
49433c02.800 brain cerebral cerebrum white matter gray matter basal ganglia fx increase intensity in gray matter relative decrease in intensity in white matter dx global ischemia question brain death probable irreversible brain death cerebral infarction s/p arrest MRI DWI diffusion weighted imaging normal and abnormal Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
|
CVS
RS
GIT
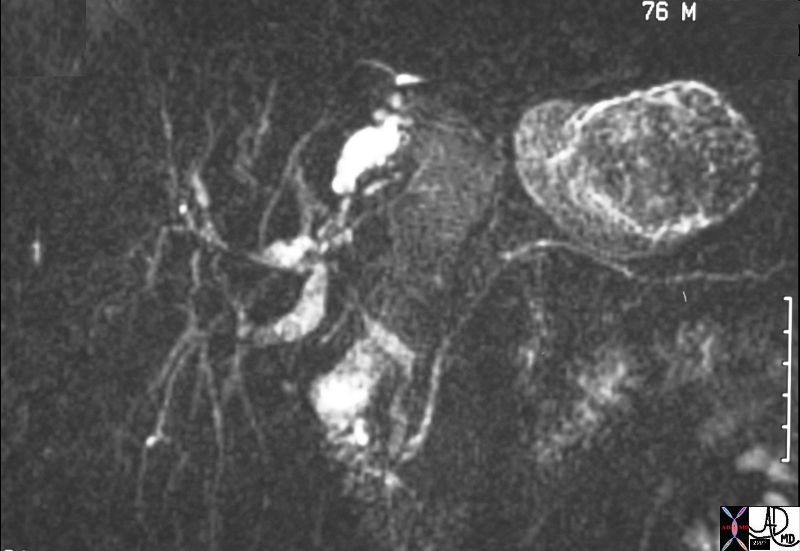
MRCP – Stenoses in Bile Ducts Caused by Sclerosing Cholangitis
|
| 24209.800 76 male with jaundice liver bile duct fx narrowed fx multicentric narrowing Dx sclerosing cholangitis chronic inflammation pancreas pancreatic duct ampulla fx normal MRI T2 weighted Davidoff MD |
GUT
MSK
RES
Skin
Calcification
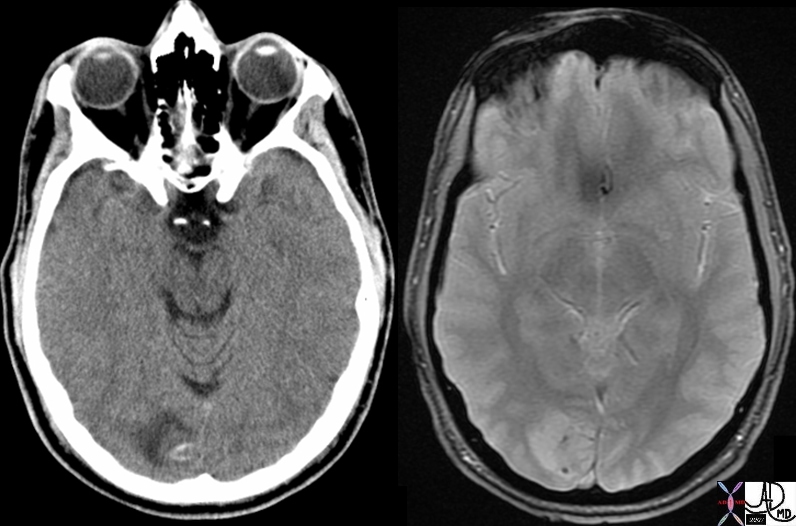
Tumor Calcification – CT dense MRI GRE Susceptibility Effects |
| 49484c01 brain cerebrum possterior aspect calcarine fissure posterior medial occipital lobe fx mass cystic fx mural nodule fx intraaxial fx calcification calcified dx neoplasm neural tumor or mixed neural glial tumor or pilocytic astrocytoma CTscan MRI GRE Davidoff MD |
Time
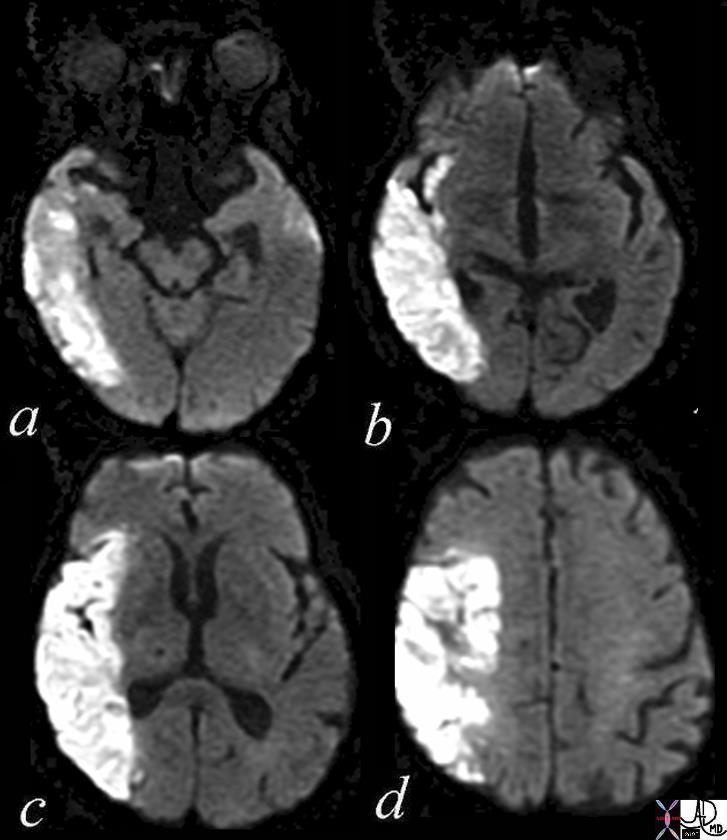
Subacute Infarction
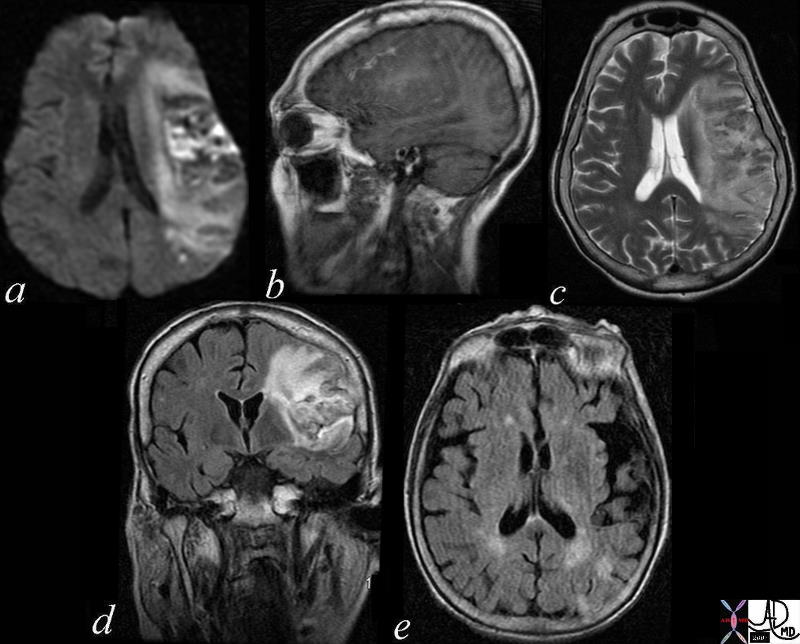
Subacute Hemorrhagic Infarction – 1 month old by history |
| 71000c03 a = DWI b= T1 c= T2 d= FLAIR e=”GRE” 70 Male extensive infarct left MCA territory which has mild mass effect on ventricles petechial hemorrhage T2 and FLAIR hyperintense T2 shine through on diffusion weighted images punctate area in left parietal lobe restricted area of diffusion question recent small infarct MRI about 1 month old from clinical presentation dx subacute hemorrhagic infarct MRI Davidoff MD |
Hemorrhage
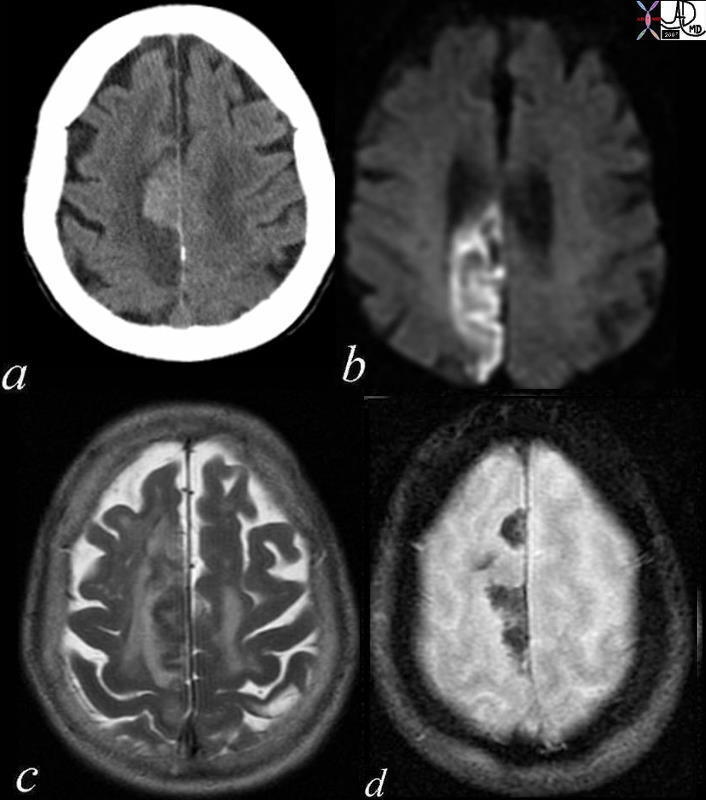
DWI
Diffusion Weighted Imaging
|
| 71275c01c03 brain cerebral infarction cerebrum mid and posterior aspects of frontal cortex most of parietal cortex involvement of insula frontal operculum cerebral acute right mca infarct parietal lobe temporal lobe right middle cerebral artery infarction DWI diffusion weighted imaging bright basal ganglia spared MRI Davidoff MD 71275c01.800 |
|














