The Common Vein copyright 2007
Definition
Nuclear medicine is an imaging technique that uses radioactive substances to evaluate structure, function and disease and it is also used in the treatment of disease.
Principles
The radioisotopes are usually tagged onto to a carrier molecule that selectively attaches to a structure in the body. The radioisotope, (aka radiopharmaceutical agent or tracer,emits gamma rays and these are detected by a gamma detector. The level of activity can be Gamma rays are that emitted from the radioactive. A computer is used to analyse the data and to produce images and measurements of organs, tissues, and lesions.
The radiopharmaceutical is usually excreted via the urinary system.
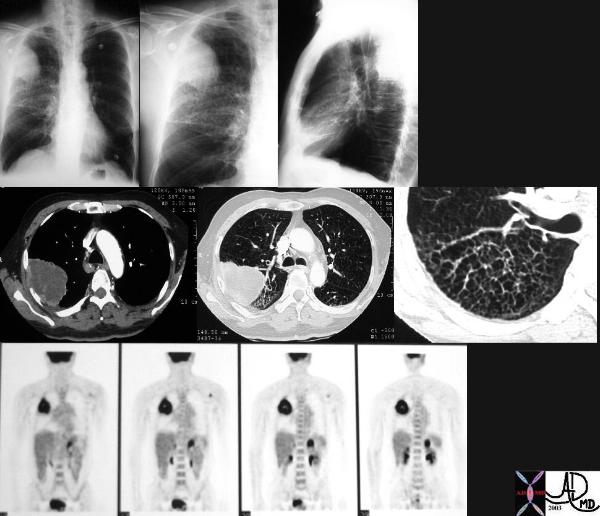
 Necrotizing Granuloma Necrotizing Granuloma |
| 72372c03 60 female with long history of smoking lung nodule slow growth SUV 1.3 right lower lobe dx necrotizing granuloma Most necrotizing granulomas are related to infection. Wegener’s granulomatosis Churg-Strauss syndrome – vasculitis sarcoidosis usually non necrotizing CTscan PETscan Davidoff MD |

HIDA scan Positive for Acute Cholecystitis |
| The scan was taken at 2 and half hours after administration of the radiosotope, and fails to show filling of the gallbladder. This finding confirmins an obstruction of the cystic duct and the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis is highly likely.
04208 gallbladder non-filling HIDA scan dx acute cholecystitis imaging radiology nuclear medicine NMscan |
Aim
To evaluate structure, function, and disease in the body, and sometimes used for targetted therapy.
Indications
Brain Scan
Endocrine System; thyroid, parathyroid, octreotide (somatostattin receptor disease such as neuroendocrine tumors)
Lung Scan; pulmonary embolism
Cardiac Imaging; blood flow, cardiac function at rest and excercise
Gastrointestinal system; GI bleeding, cholecystitis, liver tumors, bile duct patency
Genitourinary system; Assessment of renal blood flow
Musculoskeletal system; fractures, osteomyelitis, arthritis, tumor
Specific Disease Categories; infection, inflammation,malignancy

Acute GI bleed
46590 small bowel fx radioisotope leak into small bowel dx GI bleed hemorrhage Radioactibe labelled sulfur colloid Nuclear Medicine NMscan Davidoff MD
Contraindications
In pregnancy, studies during organogenesis within in the first trimester are contraindicated unless the mother’s life is threatened by the disorder. In the remaining trimesters, studies are relatively contraindicated, and clinical prudence is necessary.
Advantages
The utility related to sensitivity, specificty, and accuracy for acute cholecystitis, bile duct leakage, toxic hyperactive goiter, and acute gastrointestinal bleeding for example are superior to any other studies available for these entities
Allergies to the radiopharmaceuticals are rare.
Disadvantages
Radiation exposure. The radiopharmaceuticals do subject the patient to a small ampount of radiation but there are no known long term effects.
Nuclear medicine procedures are relatively long compared to most of the imaging procedures. Accumulation of the radiopharmaceutical can take from hours up to days and would require two vists to the department. One for injection and the second for the imaging. Imaging is also a fairly lenthy procedure and can take between 1 and 3 hours .hours to perform, depending on the study.
Method
Patient Preparation
There is no special preparation necessary prior to a study.
For the evaluation of ther stomach though the patient should be fasting for 4 hours.
For studies involving renal evaluation, the patient should drink extra water in order to flush the kidneys.
After the injection there may be a delay before imaging. Some procedures require immediate imaging while in others, there is a delay of hours and sometimes even days after the injection.
Scanning times are relatively long – and usually run between 20-45 minutes during which time it is important to lie still.
The patient usually lies prone during the procedure.
Equipment
Camera that is housed metallic casing. The design of the equipment tailored to the type of exam and the body part being imaged. It can take the form of a ring, or a single unit suspended from a bracket in the ceiling overlying the examination table, under the table, or within a doughnut.
Technique
A small dose of radioactive material is usually administered intravenously but occasionally is given orally.
Depending on the type of scan imaging will be performed either immediately, a few hours later, or several days after the injection. Imaging time varies, gbut enerally ranges from 20 to 45 minutes.
Results
Brain Scan
Endocrine System; thyroid, parathyroid, octreotide (somatostattin receptor disease such as neuroendocrine tumors)
Lung Scan; pulmonary embolism
Cardiac Imaging; blood flow, cardiac function at rest and excercise
Gastrointestinal system; GI bleeding, cholecystitis, liver tumors, bile duct patency
Genitourinary system; Assessment of renal blood flow
Musculoskeletal system; fractures, osteomyelitis, arthritis, tumor
Specific Disease Categories; infection, inflammation,malignancy
Potential Complications
The are no significant potential complications to the procedure
Conclusion
Nuclear medicine offers a safe, and sometimes unique tool in medical imaging sometimees providing the only method of accurately diagnosing a disorder. It plays a particular role in functional evaluation. Of recent, PETscanning has been a major breakthrough in the evaluation of cancer.
|
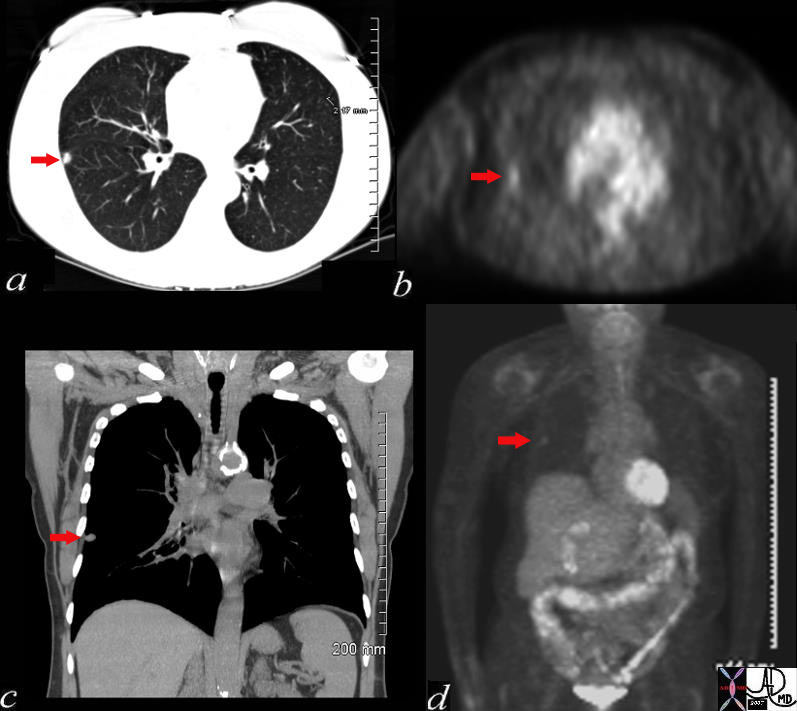
Malignant Disease in the RUL with PET positive Left Adrenal Gland – Stage 4 |
| This is a patient with lung carcinoma presenting with a large mass in the right upper lobe with a lymphangitic pattern, adrenal metastasis and a PET positive scan for the mass and for the left adrenal gland. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 32269b see 680249 code lungs pulmonary mass RUL neoplasm malignant primary lymphatics lymphangitis imaging plain film CXR CTscan PETscan |

Cisternogram |
| 49689.800 CSF flow brain cisternogram radioisotope injected into subarachnoid space via lumbar puncture and over 6.5 hours progresses to base of brain. This patient had a CSF leak in the cribiform plate. Hernose was plugged with cotton gauze and the gauze was scanned after 6 hours – The left and right were both positive for leak greater on the right nuclear medicine Courtesy Alan Ashare MD |

Melanoma |
| 49726c01.800 nodules lungs peritoneal cavity retropritoneum CT scan PET scan dx metastattic melanoma metastases Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD 49725.800 mets |

Recent Myocardial Infarction |
| 49688.800 bone heart uptake in ribs right posterior probably related to rib fractures. Finding of interest is the uptake in the heart which should not be seen with a bone scan and it indicates a recent myocrdial infarction NM radioisotope Courtesyt Alan Ashare MD |