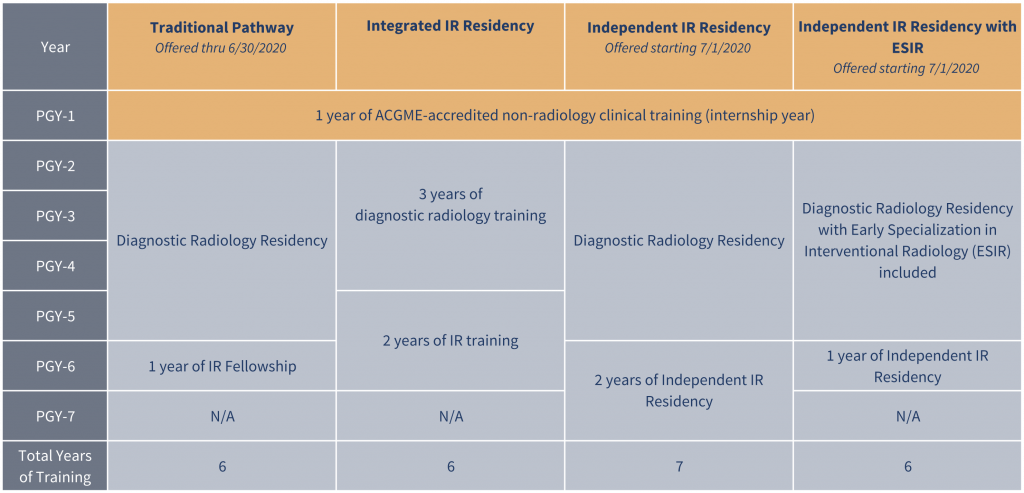
Residency Structure
- Duration:
- Integrated IR/DR Residency: 6 years, including the internship year (1 year of clinical internship + 5 years of IR training).
- Independent IR Residency: 1–2 years after completing a diagnostic radiology residency.
- Curriculum Overview:
- Diagnostic Radiology Training (PGY-2 to PGY-4):
- Rotations in general radiology, including neuroradiology, body imaging, chest radiology, musculoskeletal imaging, nuclear medicine, and breast imaging.
- Interventional Radiology Training (PGY-5 to PGY-6):
- Extensive procedural training in vascular and non-vascular interventions (e.g., biopsies, drainages, angiography, tumor ablations).
- In-depth exposure to pre- and post-procedural patient care.
- Rotations in related fields, such as vascular surgery and critical care.
- Diagnostic Radiology Training (PGY-2 to PGY-4):
Key Components for Admission
- Clinical Rotations and Evaluations:
- Strong performance in radiology and surgery electives.
- Experience in interventional radiology rotations or observerships is highly recommended.
- USMLE/COMLEX Scores:
- Competitive scores on Step 1 and Step 2 CK.
- Letters of Recommendation:
- At least one or more letters from interventional radiologists or radiology faculty.
- Letters highlighting technical aptitude, patient care skills, and interest in IR.
- Research Experience:
- Strongly valued, particularly in IR-related topics such as vascular procedures, oncology, or device development.
- Presentations or publications in radiology or IR conferences (e.g., SIR, RSNA).
- Extracurricular Activities:
- Leadership or involvement in radiology interest groups.
- Membership in professional organizations like the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR).
- Personal Statement:
- A compelling narrative explaining your interest in interventional radiology and your career goals.
- Highlight procedural interest, problem-solving skills, and patient care focus.
- Interpersonal Skills:
- Strong teamwork and communication skills, as IR physicians work closely with multidisciplinary teams.
Additional Training Opportunities
- Clinical Rotations in Related Specialties:
- Exposure to vascular surgery, oncology, hepatology, and nephrology.
- Hands-On Procedural Experience:
- Training in catheter-based procedures, embolization, ablation, and stent placements.
- Technical Proficiency:
- Familiarity with imaging modalities (fluoroscopy, ultrasound, CT, MRI) and advanced technologies (robotics, AI).
Board Certification Requirements
- Dual Certification:
- Graduates of an IR residency program are eligible for dual certification in both Interventional Radiology and Diagnostic Radiology by the ABR.
- Examinations:
- Core Exam (taken during residency).
- Final Certifying Exam (covers both diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology).
Key Takeaways
IR residency programs seek candidates with strong diagnostic radiology skills, technical aptitude, and a clear interest in interventional procedures. Applicants should demonstrate a balance of academic excellence, research, and clinical exposure to interventional radiology.
Links
ABR IR Residency Considerations